New Publication: An Automated MicroScale Thermophoresis Screening Approach for Fragment-Based Lead Discovery
Fragment-based lead discovery has proved to be an effective alternative to high-throughput screenings in identifying chemical matter that can be developed into robust lead compounds.
This publication describes an approach utilizing automated MicroScale Thermophoresis (MST) affinity screening to identify fragments active against MEK1 kinase. MST identifies multiple hits that were confirmed by X-ray crystallography but not detected by orthogonal methods. Furthermore, MST also provided information about ligand-induced aggregation and protein denaturation.
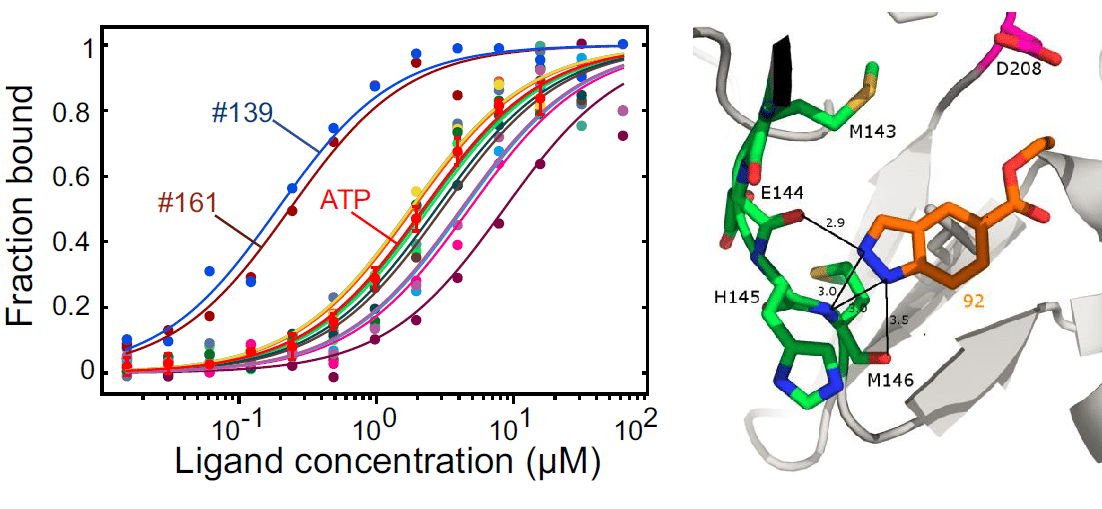
Combining speed and low material requirements with the reliable identification of true binders by deriving binding affinities, MST has been demonstrated to be an effective method for screening fragments. Used in conjunction with other biophysical techniques, MST has the potential to significantly improve FBLD workflows.
Click here to read the full publication.
